| A abbr. 1. accusative 2. Games ace 3. across 4. adenine 5. alto 6. ampere 7. or Å angstrom 8. area |
a 1 or A ( ) ) n. pl. a's or A's also as or As Idiom:1. The first letter of the modern English alphabet. 2. Any of the speech sounds represented by the letter a. 3. The first in a series. 4. Something shaped like the letter A. 5. A The best or highest in quality or rank: grade A milk. 6. Music a. The sixth tone in the scale of C major or the first tone in the relative minor scale. b. A key or scale in which A is the tonic. c. A written or printed note representing this tone. d. A string, key, or pipe tuned to the pitch of this tone. 7. A One of the four major blood groups in the ABO system. Individuals with this blood group have the A antigen on the surface of their red blood cells, and the anti-B antibody in their blood serum. from A to Z Completely; thoroughly. |
a 2 (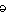 ; ;  when stressed) when stressed) indef.art. 1. Used before nouns and noun phrases that denote a single but unspecified person or thing: a region; a person. 2. Used before terms, such as few or many, that denote number, amount, quantity, or degree: only a few of the voters; a bit more rest; a little excited. 3. a. Used before a proper name to denote a type or a member of a class: the wisdom of a Socrates. b. Used before a mass noun to indicate a single type or example: a dry wine. 4. The same: birds of a feather. 5. Any: not a drop to drink. Usage Note: In writing, the form a is used before a word beginning with a consonant sound, regardless of its spelling (a frog, a university). The form an is used before a word beginning with a vowel sound (an orange, an hour).·An was once a common variant before words beginning with h in which the first syllable was unstressed; thus 18th-century authors wrote either a historical or an historical but a history, not an history. This usage made sense in that people often did not pronounce the initial h in words such as historical and heroic, but by the late 19th century educated speakers usually pronounced initial h, and the practice of writing an before such words began to die out. Nowadays it survives primarily before the word historical. One may also come across it in the phrases an hysterectomy or an hereditary trait. These usages are acceptable in formal writing. |
a 3 (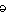 ) ) prep. In every; to each; per: once a month; one dollar a pound. |
a 4 (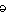 ) ) aux.v. Informal Have: He'd a come if he could. [Middle English, alteration of haven, to have; see have.] |
| a 5 abbr. 1. acceleration 2. are (measurement) |
The American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition copyright ©2000 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Updated in 2003. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
a or A
a
A
| A Abbreviation of adenine, ampere, angstrom, area |
| Å Abbreviation of angstrom |
The American Heritage® Science Dictionary Copyright © 2005 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
| Noun | 1. | A - a metric unit of length equal to one ten billionth of a meter (or 0.0001 micron); used to specify wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation metric linear unit - a linear unit of distance in metric terms micromillimeter, micromillimetre, millimicron, nanometer, nanometre, nm - a metric unit of length equal to one billionth of a meter |
| 2. |  A - any of several fat-soluble vitamins essential for normal vision; prevents night blindness or inflammation or dryness of the eyes A - any of several fat-soluble vitamins essential for normal vision; prevents night blindness or inflammation or dryness of the eyes fat-soluble vitamin - any vitamin that is soluble in fats retinol, vitamin A1 - an unsaturated alcohol that occurs in marine fish-liver oils and is synthesized biologically from carotene dehydroretinol, vitamin A2 - a viscous alcohol that is less active in mammals than is vitamin A1 | |
| 3. | A - one of the four nucleotides used in building DNA; all four nucleotides have a common phosphate group and a sugar (ribose) nucleotide, base - a phosphoric ester of a nucleoside; the basic structural unit of nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) | |
| 4. | A - (biochemistry) purine base found in DNA and RNA; pairs with thymine in DNA and with uracil in RNA biochemistry - the organic chemistry of compounds and processes occurring in organisms; the effort to understand biology within the context of chemistry purine - any of several bases that are derivatives of purine deoxyribonucleic acid, desoxyribonucleic acid, DNA - (biochemistry) a long linear polymer found in the nucleus of a cell and formed from nucleotides and shaped like a double helix; associated with the transmission of genetic information; "DNA is the king of molecules" ribonucleic acid, RNA - (biochemistry) a long linear polymer of nucleotides found in the nucleus but mainly in the cytoplasm of a cell where it is associated with microsomes; it transmits genetic information from DNA to the cytoplasm and controls certain chemical processes in the cell; "ribonucleic acid is the genetic material of some viruses" | |
| 5. | A - the basic unit of electric current adopted under the Systeme International d'Unites; "a typical household circuit carries 15 to 50 amps" current unit - a measure of the amount of electric charge flowing past a circuit point at a specific time milliampere, mA - one thousandth of an ampere | |
| 6. |  a - the 1st letter of the Roman alphabet a - the 1st letter of the Roman alphabet Latin alphabet, Roman alphabet - the alphabet evolved by the ancient Romans which serves for writing most of the languages of western Europe alphabetic character, letter of the alphabet, letter - the conventional characters of the alphabet used to represent speech; "his grandmother taught him his letters" | |
| 7. |  A - the blood group whose red cells carry the A antigen A - the blood group whose red cells carry the A antigen blood group, blood type - human blood cells (usually just the red blood cells) that have the same antigens |
 Translations
TranslationsState manager I ICMAS
Abacus brain Study pvt.Ltd
Road no-10 I Banjara hills I Hyderabad
Samuel Goldwyn - "I had a monumental idea this morning, but I didn't like it."

 their feathers
their feathers bird - warm-blooded egg-laying vertebrates characterized by feathers and forelimbs modified as wings
bird - warm-blooded egg-laying vertebrates characterized by feathers and forelimbs modified as wings bird - informal terms for a (young) woman
bird - informal terms for a (young) woman  bird - a cry or noise made to express displeasure or contempt
bird - a cry or noise made to express displeasure or contempt bird - badminton equipment consisting of a ball of cork or rubber with a crown of feathers
bird - badminton equipment consisting of a ball of cork or rubber with a crown of feathers




